Indispensable for optimized SEO indexing, META robots tags are designed to provide guidelines for search engine crawlers. So what are these guidelines, and how do they affect the ranking of your web pages in Google?
META robots tags are an important element to take into account in your search engine optimization (SEO) strategy. They allow you to control how search engines index and display the content of your website, which can have a significant impact on your site’s visibility in search results.
What is a META robots tag?
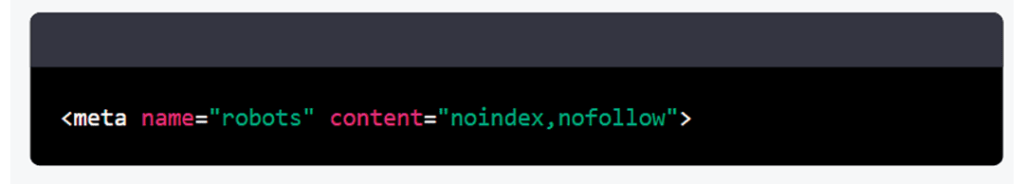
A META robots tag is an HTML tag that allows webmasters to control how search engines index and display the content of a website. It is located in the header of the HTML document and is used to indicate to search engine spiders whether or not they are allowed to index and track the content of the site. For example, the following tag tells robots not to index the content of the page and not to follow the links on the page:
Placed in the header of a page’s code (HEAD), the META robot tag provides guidance to search engines. It has a major impact on the SEO indexing and visibility of each page thanks to a number of guidelines for crawlers, and more specifically for Googlebot and BingBot.
While the presence of SEO robot META tags is therefore essential, they should be used with full knowledge of the facts, as some of them are designed to prevent content from appearing in the SERPs.
How to use an SEO tag?
It is important not to rely solely on META robots tags to control the indexing and tracking of your site by search engines. It is advisable to combine the use of these tags with other SEO techniques, such as setting up link deletion files or using nofollow tags for external links.
By making judicious use of META robots tags, you can improve your site’s ranking in the search results and ensure that only content that is relevant to your audience is displayed in the search results. Don’t forget, however, that it’s important to follow the search engine guidelines and not try to trick their algorithms by misusing these tags – adding a tag is not something that can be done so quickly. Good referencing is based above all on the quality and relevance of the content provided, for example with a good description of the site or optimized tags (h1 tag, title tag or alt tag, etc.).
Got an SEO question?
Julia can help
7 years of SEO expertise

META robots SEO: the different directives
The META tag on each page of a site may be different and may consist of one or more directives intended for all or some of the search engines.
There are several possible values for the robots META tag, including “index”, “noindex”, “follow”, “nofollow”, “none” and “all”. These values are used to control whether robots can index the content of the page, follow the links on the page, or both. The META robots tag is mainly used to prevent search engines from indexing content that is not intended to be displayed in search results, such as test pages or duplicate content pages.
Noindex and index
The Noindex directive tells the bots that the page should be ignored and not appear in the SERPs. It is widely used to block the indexing of a URL whose content may be duplicated, thus avoiding any risk of Google penalties (particularly Google Panda).
In contrast, the index directive stipulates to search engines that indexing of content is desirable. Logically, this is of little use, since if there are no instructions to the contrary (noindex), the spider will crawl the page.
Nofollow and follow
The nofollow directive is probably the one that divides the SEO community the most. In theory, it allows you to indicate to Google Bots that you don’t want the links within the page to be followed, in particular because they have no weight or authority. However, it can also be argued that this does not necessarily send a positive signal to Google, which in any case treats the information as it wishes.
Conversely, by specifying the follow directive in a robot META tag, SEO indexation of the links is expressly requested.
Noarchive and archive
Noarchive is a directive asking Google not to cache the page. This means that users cannot access a previous version of the URL, which is extremely practical for a shop that regularly revises its prices, for example according to the value of the dollar.
The archive directive tells Google that the site owner wants his URL to be cached for search engines.
As far as Bing is concerned, nocache and cache should be used instead of noarchive and archive respectively.
None and all
The none directive allows you to ask SEO robots to ignore the page completely. As a result, the page is not indexed in the SERPs and the links to which it points are not followed.
Conversely, by indicating all in a tag, you are indicating that you want the page to be indexed and the links followed. In practice, there is no reason to add it, since in the absence of a directive to the contrary, the crawler will logically perform both these actions.
Nosnippet
By adding the Nosnippet directive to a robot META tag, it is requested that snippets are not indexed in search results, nor are they cached.
Notranslate
The notranslate directive requires that no automatic translation is available for the page.
Unavailable_after:{date}
Unavailable_after:[date] is a slightly unusual directive, as it tells SEO robots that content can be indexed in the SERPs, but only for a given period of time. After the specified date, it can no longer be accessed. This can be very useful in the case of a flash sale, for example.
It should also be noted that it is possible to provide different instructions to Google and Bing :
- META robot for all search engines ;
- META robot for Google only;
- META robot for Bing only.
META robots are one of the fundamental elements of any good long-term visibility strategy. To boost your natural referencing, take advantage of our digital agency’s expertise by requesting a free SEO audit.