The canonical URL tells search engine spiders which is the original copy of a web page. A tag integrated into the HTML code is used to specify to crawlers that the page is canonical, so that they do not index other pages, even if the content is duplicated.
Roughly organising these URLs can lead to serious problems that have a negative impact on your site’s performance.
The canonical URL helps solve duplicate content problems to improve your website’s SEO.
SEO.fr explains in detail how the canonical URL works and what it is used for.
What is a canonical URL?
The canonical URL is the address of a page that search engines are asked to consider as original. A canonical is therefore an HTML tag placed in the header of each duplicated page.
It is also known as a rel=”canonical”, meta canonical, canonical tag or canonical tag.
Essential protection against duplicate content
Did you know that your text, or even your entire web page, can be copied and republished as is on other sites, either for advertising purposes or as plagiarism? This problem is widespread and can affect all editorial content.
The more relevant your content, the greater the risk of duplicate content!
Unfortunately, crawlers cannot yet identify the duplication of the original. To avoid being unfairly penalised, tell Google that your page is the original using the canonical URL.
The canonical URL is also compatible with pagination. You can therefore implement a canonical URL on every page of your website.
Setting up a canonical URL
The webmaster will tell Google the address in the format and between the and tags. This will enable it to recognise similar pages created after the original as non-original and to consider only the incumbent when indexing pages. This selection is doubly beneficial: it does justice to the original content and avoids an overload of indexed pages in the search engine database.
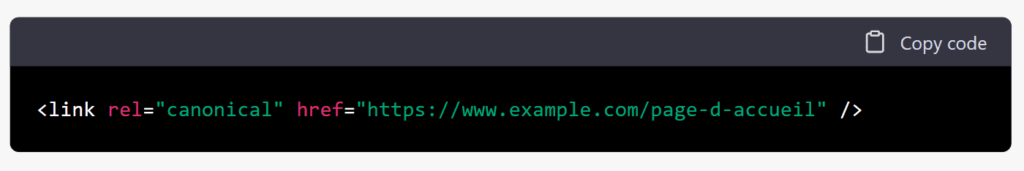
Poor mark-up or an attribute error can harm the indexing of your web page. However, most CMS platforms make the task easier.
This technical manipulation makes it possible to identify similar pages created after the original page. They are then considered as non-original and are not indexed as holders.
This operation is doubly beneficial:
- It does justice to the original content and boosts its popularity;
- It avoids overloading the search engine database with indexed pages.
Before you start, consider using Google webmaster tools to see your site as the search engine spiders see it.
Why should you always pay attention to your URLs?
The canonical URL is used to protect against content theft and is not a 301 redirect
Obviously, the ideal would be to canonicalise all the pages on your site. On the one hand, this is necessary when you have to create internal duplicate pages, duplicate a page n times, as in the case of a product data sheet for example, so that when Google indexes the pages it can choose the most valuable in terms of SEO.
This is also useful when the text on this page is likely to be used by other writers to create their own content and, above all, because certain robots are tasked with automatically stealing content to feed other sites. This will be the canonical page that the search engine will display in the search results pages for a given query. As a user, seeing identical content on several pages can slow down and cause a bounce rate.
Got an SEO question?
Géraldine can help
5 years of SEO expertise

The special nature of e-commerce sites
It should be noted that this solution is very similar to 301 redirection, which causes the search engine to choose one page over another. The difference is that the canonical URL is intended solely for search engines and is for indexing purposes, whereas the 301 redirect simply sends search engines and users from an old page to a new one, which is more like an update.
The more interesting the information concerned, the greater the duplication. However, the search engine algorithm does not like duplicate content and penalises it by denying it access to the SERPs (search results pages). The problem is that the original page runs the risk of being mistaken by robots such as Google bot for one of the duplicated pages. To overcome this problem, the Google engine offers a solution to webmasters, which is to indicate the original page as canonical as soon as it is created.
The usefulness of making this distinction lies in the relevance of the choice of technique for redirecting users or engines.
Mistakes to avoid if you want to maximise the benefits of canonical URLs
- Do not enter a canonical URL that points to a 301 redirect: instead, implement your canonical URL on the target page of the redirect.
- Do not enter non-canonical URLs in a sitemap file. Google assumes that URLs defined in a sitemap are necessarily canonical.
- Never use the canonical tag to establish a link to different content. If crawlers judge this link to be irrelevant, you will be penalised.
- Never use more than one canonical tag for each page. The crawlers won’t bother indexing them.
- Above all, don’t include two canonical tags in the of your page (be careful if you replace the default values in your cms).
Finally, don’t forget to check that Google takes your canonical URL into account by using the URL inspector in Google search console or other online webmaster tools.
You don’t know anything about source code, you’re afraid to intervene on your own and make a mistake that could harm your site’s natural referencing? SEO.fr can help, contact our experts.