The use of semantic tags is part of an overall SEO strategy. They help increase organic traffic and click-through rates. Unfortunately, they are not always taken into account on websites. We tend to focus on-page optimization, page titles and meta-description. While all these different elements are essential for SEO, exploiting structured data (microdata) can also help. How can it help?
Microdata allows you to indicate the meaning of your content to Google and other search engines. It makes it easier for indexing robots to crawl your pages. They can then interpret the data and display it in the SERP in the form of enriched extracts. What are the benefits, what impact does it have on SEO, and how do you implement semantic tags? In this article, SEO.fr reveals what lies behind structured data technology.
What is microdata? What you need to keep
Microdata refers to a specific type of tag that is integrated into the HTML code of a web page. They use an HTML 5 tag style to assign a category to the data to be structured. These are new types of metadata born of the semantic web. They provide context and additional meaning to the content of a web page. In effect, they provide the algorithm with a superior understanding of your pages’ content, and enable it to use the data to deliver a more dynamic browsing experience.
They use the simple attributes built into HTML tags. This gives them the power to assign names and descriptions to elements and properties. When no tags are present, generic tags such as span tags or the div container are used.
Different types of structured data can be used to enable search engines to understand information more precisely. This makes them much more intelligent. For example, they can tell when a web page is about :
- People: this may require you to provide exclusive data relating to the person concerned. Surname, first name, gender, education, etc.
- Recipes: in this case, microdata is used to highlight cooking times. Ingredients. Recipe preparation stages, type of cooking, etc.
- Local businesses: structured data can be used to specify opening and closing hours, address, e-mail, contact details, name, etc.
- Events: microdata can be used to specify name, period, actors, organizer, location, etc.
- Products: semantic tags are used to indicate price, brand, model, category, customer reviews, etc.

Why use semantic markup on content pages?
Microdata is used to indicate the type and value of each page to browsers. In so doing, it helps robots instantly understand the information available on your site’s pages. The result is improved indexing and natural referencing.
Structured data is used to highlight content in search results. By filling in semantic tags, you enable the search engine to create a Rich Snippet. In other words, you enable the rich snippet to be implemented, and the algorithm provides the surfer with additional information to help him or her determine whether a page is relevant to his or her query. The use of microdata is therefore part of an overall SEO strategy. They add a special touch, although they’re not enough on their own to improve a site’s SEO. They do, however, help you optimize your pages.
It may not seem obvious, but search engines are able to index sites without understanding their content. They detect important terms on pages and no longer rely on traditional keywords. This is how they position sites in the search results. Natively, they don’t have the ability to understand the meaning of texts. Adding clear tags brings greater precision and comprehension.
What are the main benefits of implementing semantic tags for your site?
The use of semantic tags offers a number of significant benefits. You improve the readability of web page content. Structured data has a well-defined architecture that makes web pages aesthetically pleasing to browse. This makes data exploration accessible to search engines and web users alike. It also optimizes the user experience, as navigation is dynamic.
What’s more, you make it easier to understand the data and process the text on your sites. When you implement microdata on your web pages, you enable indexing robots to automatically analyze your content. This enables them to index and reference your site appropriately in the SERP in a variety of formats:
- Carousel: presented as images with captions linked to a specific search. Clicking on these images takes the user to a separate SERP for each search.
- Video: similar to carousels, but displaying only videos.
- Snippet: the enriched snippet contains information relevant to a query and a link to a website. It can feature quotes, tables, etc.
- Knowledge panel: stands out for its location. It appears on the right-hand side of search results. It can include images, dates, information, etc.
But what impact does structured data have on your site’s SEO?
Microdata have a positive influence on the SEO of a web page, as they organize the content displayed on search engines. They also enhance the user experience. When you integrate them into your site, Google is able to understand the type of content on your pages. It can then reward you and generate optimized results for web users thanks to microdata.
With clear tags, you help robots to identify the breadcrumb trail and easily recognize the tree structure of your HTML documents. This helps your pages to stand out from the crowd and to be displayed in results enriched with structured data. Once you’ve secured the top positions 0 on the first page, you’ll significantly improve your click-through rate (CTR).
The use of structured data can have a real positive effect on your positioning. If your site’s URL is positioned in the top 5 results on the first page of Google, it will receive more clicks and may even reach position zero. To achieve this, the response element you provide through your content must be rich and relevant according to the algorithms’ criteria.
What’s more, by providing precise information to search engines, microdata enable you to attract visitors interested in your content. This can, to some extent, reduce the load on the web server and have a positive impact on site loading times. It’s also a great way of reducing the bounce rate on your website.
Ultimately, structured data is a tool for SEO experts, web developers and search engine optimization specialists. They can help improve a website’s visibility in search engines.
Got a question about SEO?
Julia can help
8 years of SEO expertise

How do you integrate microdatas into the source code of your website pages?
Microdata can add value to your SEO strategy. However, it’s not enough to master HTML and CSS to generate them. While it’s essential to know HTML, you need to be able to distinguish between the different formats of structured data. Then, you’ll choose the right format according to the requirements of your CMS.
Google authorizes 3 structured data formats:
- JavaScript : Object Notation for Linked Data (JSON-LD). This is a simple W3C-standard website technique that helps you implement structured data using the JSON symbol.
- Microdata: this HTML specification is placed around the content to be enriched. It uses the attributes of HTML tags to identify the various properties required.
- RDFa: refers to Resource Description Framework in Attributes. It uses HTML5 tag attributes and assigns names to properties to be declared as structured data.
In addition to format selection, you’ll need tools to generate structured data markup. You’ll also need them to check that the microdata is working properly. Take inspiration from the documentation available on Schema.org to create semantic tag codes. In addition, use Google’s tagging tool.
The best Schema markup generators available online can also be assets. Have you finished generating your markup codes? Now you need to check that they work. Google’s structured data test tool comes in handy for this. You can also use Search Console, which features an “improvement” menu where you’ll see errors and details relating to your URLs.
Discover now the 5 best microdatas to insert on your website pages
Schema.org: the result of collaboration between major search engines such as Google, Bing, Yahoo and Yandex. It provides a standard set of microdata types. It offers a wide range of tags for different types of content, including articles, events, products, comments, organizations and more. Schema.org is highly recommended for implementing structured data on websites.
1. Product : If you own an e-commerce store, it’s essential to implement structured data for product information. This includes details such as product name, description, price, availability, ratings and reviews.
<html>
<head>
<title>Executive Anvil</title>
</head>
<body>
<div>
<div itemtype="https://schema.org/Product" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="mpn" content="925872" />
<meta itemprop="name" content="Executive Anvil" />
<link itemprop="image" href="https://example.com/photos/16x9/photo.jpg" />
<link itemprop="image" href="https://example.com/photos/4x3/photo.jpg" />
<link itemprop="image" href="https://example.com/photos/1x1/photo.jpg" />
<meta itemprop="description" content="Sleeker than ACME's Classic Anvil, the Executive Anvil is perfect for the business traveler looking for something to drop from a height." />
<div itemprop="offers" itemtype="https://schema.org/Offer" itemscope>
<link itemprop="url" href="https://example.com/anvil" />
<meta itemprop="availability" content="https://schema.org/InStock" />
<meta itemprop="priceCurrency" content="USD" />
<meta itemprop="itemCondition" content="https://schema.org/UsedCondition" />
<meta itemprop="price" content="119.99" />
<meta itemprop="priceValidUntil" content="2020-11-20" />
</div>
<div itemprop="aggregateRating" itemtype="https://schema.org/AggregateRating" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="reviewCount" content="89" />
<meta itemprop="ratingValue" content="4.4" />
</div>
<div itemprop="review" itemtype="https://schema.org/Review" itemscope>
<div itemprop="author" itemtype="https://schema.org/Person" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="name" content="Fred Benson" />
</div>
<div itemprop="reviewRating" itemtype="https://schema.org/Rating" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="ratingValue" content="4" />
<meta itemprop="bestRating" content="5" />
</div>
</div>
<meta itemprop="sku" content="0446310786" />
<div itemprop="brand" itemtype="https://schema.org/Brand" itemscope>
<meta itemprop="name" content="ACME" />
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>Here is the HTML code if a page sells a product and contains product reviews
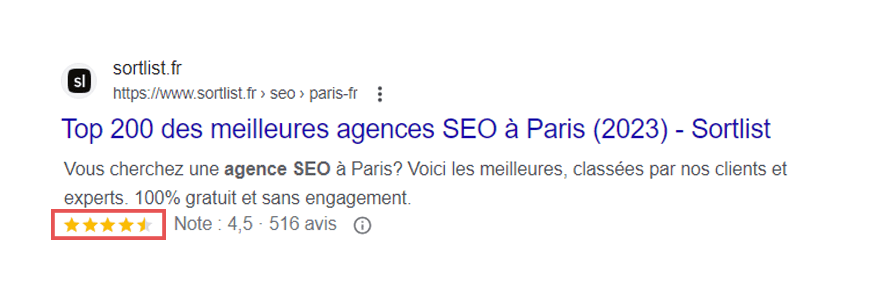
2. Stars: This microdata helps to improve the visibility and relevance of pages in search results, which can increase click-through rates and user confidence in content.
<html>
<head>
<title>Executive Anvil</title>
</head>
<body>
<div itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/Product">
<span itemprop="brand" itemtype="https://schema.org/Brand" itemscope>ACME</span> <span itemprop="name">Executive Anvil</span>
<img itemprop="image" src="https://example.com/photos/1x1/anvil_executive.jpg" />
<span itemprop="aggregateRating" itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/AggregateRating">
Average rating: <span itemprop="ratingValue">4.4</span>, based on
<span itemprop="ratingCount">89</span> reviews
</span>
<span itemprop="offers" itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/AggregateOffer">
from $<span itemprop="lowPrice">119.99</span> to
$<span itemprop="highPrice">199.99</span>
<meta itemprop="priceCurrency" content="USD" />
</span>
</div>
</body>
</html>Here is the HTML code if a page contains a product with rated reviews
3. Breadcrumbs: Breadcrumbs are a form of microdata that show the hierarchical structure of a website’s pages. They provide users with a trail of links enabling them to navigate back to previous pages. Breadcrumbs not only enhance the user experience. They also give search engines a better understanding of the site’s structure and hierarchy.
<html>
<head>
<title>Award Winners</title>
</head>
<body>
<ol itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/BreadcrumbList">
<li itemprop="itemListElement" itemscope
itemtype="https://schema.org/ListItem">
<a itemprop="item" href="https://example.com/books">
<span itemprop="name">Books</span></a>
<meta itemprop="position" content="1" />
</li>
›
<li itemprop="itemListElement" itemscope
itemtype="https://schema.org/ListItem">
<a itemscope itemtype="https://schema.org/WebPage"
itemprop="item" itemid="https://example.com/books/sciencefiction"
href="https://example.com/books/sciencefiction">
<span itemprop="name">Science Fiction</span></a>
<meta itemprop="position" content="2" />
</li>
›
<li itemprop="itemListElement" itemscope
itemtype="https://schema.org/ListItem">
<span itemprop="name">Award winners</span>
<meta itemprop="position" content="3" />
</li>
</ol>
</body>
</html>Here is the HTML code if a page contains a breadcrumb trail
4. Local businesses: If your website represents a local business, it’s essential to implement data structures specific to local business information. This includes details such as business name, address, phone number, opening hours and customer reviews. All this enriched data helps local search engines and directories. They accurately display information about your organization in search results.
<html>
<head>
<title>Trattoria Luigi</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org/",
"@type": "Restaurant",
"name": "Trattoria Luigi",
"image": [
"https://example.com/photos/1x1/photo.jpg",
"https://example.com/photos/4x3/photo.jpg",
"https://example.com/photos/16x9/photo.jpg"
],
"priceRange": "$$$",
"servesCuisine": "Italian",
"address": {
"@type": "PostalAddress",
"streetAddress": "148 W 51st St",
"addressLocality": "New York",
"addressRegion": "NY",
"postalCode": "10019",
"addressCountry": "US"
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Here is the HTML code for a restaurant in carousel format
5. Article: Article metadata is information that provides specific details about the content of the article. This metadata helps search engines to understand the subject, title, author, publication date and other important information about the article.
<html>
<head>
<title>Title of a News Article</title>
<script type="application/ld+json">
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "NewsArticle",
"headline": "Title of a News Article",
"image": [
"https://example.com/photos/1x1/photo.jpg",
"https://example.com/photos/4x3/photo.jpg",
"https://example.com/photos/16x9/photo.jpg"
],
"datePublished": "2015-02-05T08:00:00+08:00",
"dateModified": "2015-02-05T09:20:00+08:00",
"author": [{
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Jane Doe",
"url": "https://example.com/profile/janedoe123"
},{
"@type": "Person",
"name": "John Doe",
"url": "https://example.com/profile/johndoe123"
}]
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>Here is the HTML code for an article containing microdata